- Home
- Services
Our experienced team of developers and designers works closely with you to understand your needs and deliver high-quality, scalable, and user-friendly software applications.
- Solutions
- About Us
- Contact Us
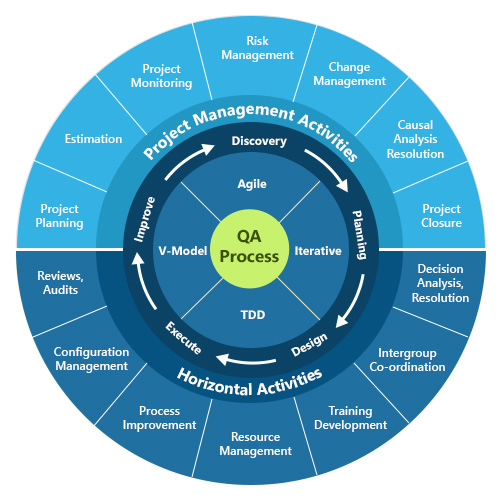
Process of Quality Assurance and Testing
"Quality means doing it right when no one is looking."
Testing and Quality Asuurance Process
Requirement Analysis:
- Understand and analyze the requirements provided by stakeholders or clients to determine the expected behavior and functionality of the software product.
Test Planning:
- Develop a comprehensive test plan outlining the testing approach, objectives, scope, resources, timelines, and deliverables.
- Identify test scenarios, test cases, and testing techniques based on the requirements and project specifications.
Test Environment Setup:
- Set up the necessary hardware, software, and testing tools required to execute the planned tests effectively.
- Create test data and establish test environments that closely resemble the production environment.
Test Case Design:
- Define detailed test cases covering various functional and non-functional aspects of the software, including positive and negative scenarios, edge cases, and boundary conditions.
- Ensure that test cases are clear, specific, and executable, with expected outcomes and criteria for pass/fail evaluation.
Test Execution:
- Execute the planned tests according to the test plan and test cases, using manual or automated testing techniques.
- Record test results, including any defects, issues, or deviations from expected behavior, in a test management tool or defect tracking system.
Defect Reporting and Management:
- Document and report identified defects or issues, providing detailed descriptions, steps to reproduce, severity, and priority.
- Collaborate with development teams to investigate, prioritize, and address reported defects, ensuring timely resolution and closure.
Regression Testing:
- Perform regression testing to verify that recent changes or fixes have not introduced new defects or caused unintended side effects.
- Re-run selected test cases or test suites to validate the stability and integrity of the software across multiple iterations or releases.
Performance Testing:
- Evaluate the performance, scalability, and responsiveness of the software under different workload conditions, including stress testing, load testing, and endurance testing.
- Identify and address performance bottlenecks, resource constraints, and optimization opportunities to improve system efficiency and reliability.
Security Testing:
- Assess the security posture of the software by identifying vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and threats through techniques such as penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and code analysis.
- Implement security best practices and controls to mitigate risks and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or exploitation.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT):
- Involve end-users, stakeholders, or domain experts in executing acceptance tests to validate that the software meets business requirements, user needs, and expectations.
- Gather feedback, insights, and usability issues from UAT participants to inform further improvements or refinements to the software.
Documentation and Reporting:
- Document testing processes, procedures, and outcomes in test reports, summaries, or documentation artifacts.
- Provide stakeholders, clients, or project sponsors with regular updates on testing progress, status, and findings, facilitating informed decision-making and transparency.
Continuous Improvement:
- Continuously review and evaluate the effectiveness of the testing and QA process, identifying areas for improvement, optimization, and automation.
- Incorporate lessons learned, best practices, and feedback from previous testing cycles to enhance quality assurance practices and deliver higher-quality software products in future iterations.
By following a systematic and structured testing and QA process, software development teams can detect and address defects early in the development lifecycle, minimize risks, and deliver reliable, high-quality software solutions that meet user expectations and business objectives.